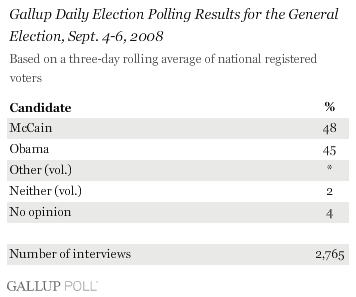
PRINCETON, NJ — The latest Gallup Poll Daily tracking update shows John McCain moving ahead of Barack Obama, 48% to 45%, when registered voters are asked for whom they would vote if the presidential election were held today.
These results are based on Sept. 4-6 interviewing, and include two full days of polling after the conclusion of the Republican National Convention last Thursday night. McCain has outpolled Obama on both Friday and Saturday, and is receiving a convention bounce just as Obama did last week.
Tomorrow’s report will be the first in which all interviews were conducted after the conclusion of the convention. Gallup measures convention bounces by comparing candidate support in the last poll done entirely before a party’s presidential nominating convention begins with the first polling conducted entirely after its conclusion.
McCain’s 48% share of the vote ties for his largest since Gallup tracking began in early March. He registered the same level of support in early May. This is also McCain’s largest advantage over Obama since early May, when he led by as much as six percentage points. Obama has led McCain for most of the campaign, and for nearly all of the time since clinching the Democratic nomination in early June. (To view the complete trend since March 7, 2008, click here.) — Jeff Jones
(Click here to see how the race currently breaks down by demographic subgroup.)
Ethiopian ReviewVisit Site
Howdy, ethiopianreview.com! | Log Out | Help | Forums |
Survey Methods
For the Gallup Poll Daily tracking survey, Gallup is interviewing no fewer than 1,000 U.S. adults nationwide each day during 2008.
The general-election results are based on combined data from Sep. 4-6, 2008. For results based on this sample of 2,765 registered voters, the maximum margin of sampling error is ±2 percentage points.
Interviews are conducted with respondents on land-line telephones (for respondents with a land-line telephone) and cellular phones (for respondents who are cell-phone only).
In addition to sampling error, question wording and practical difficulties in conducting surveys can introduce error or bias into the findings of public opinion polls.
